McCormick Place, Lakeside Center
Sunday, September 25, 2005
9:00 AM - 5:00 PM
McCormick Place, Lakeside Center
Monday, September 26, 2005
9:00 AM - 5:00 PM
McCormick Place, Lakeside Center
Tuesday, September 27, 2005
9:00 AM - 5:00 PM
McCormick Place, Lakeside Center
Wednesday, September 28, 2005
9:00 AM - 5:00 PM
8226
Alloderm (Acellular Human Dermis) in Breast Reconstruction with Tissue Expansion
Introduction: Alloderm (Life Cell, N.J.) is an acellular dermis allograft that is processed to have all antigenic stimuli removed. Alloderm is widely used in reconstructive procedures, but has not been widely reported in breast reconstruction. We have hypothesized that Alloderm in breast reconstruction with tissue expanders will lead to a larger initial expansion, great patient satisfaction, and lower complication rate. Methods: A review of all patients who had Alloderm placed during breast reconstruction with tissue expander (TE) from April 2004 to February 2005 was undertaken. All patients had a mastectomy for treatment of breast carcinoma, sarcoma or for prophylaxis. An Integra (PMT,C.MM) anatomical textured TE was placed in the sub-pectoralis space. A medium thickness 12x4 cm, allograft was sutured along the inferolateral pectoralis muscle edge and serratus anterior muscle, using continued running 3-0 Vycril suture (Ethicon, S, NJ). Elevation of the serratus anterior muscle was not necessary. The TE was partially injected with Normal Saline (NS). The quantity of NS injected varied to avoid undue tension on the healing skin flaps. Upon the completion of the expansion, in a second stage the TE was exchanged for a smooth round saline implant (Mentor, SB, CA). Results: Thirty patients had 48 mastectomies followed by reconstruction. Average age was 44 years (30-70y). Eleven patients had unilateral mastectomy and 19 had bilateral. Twenty-nine (60.4%) mastectomies were performed for cancer and 19 (39.6%) for prophylaxis. Neo-adjuvant chemotherapy was administered in 4 (13 %) patients and post operative chemotherapy in 9 (30 %). Forty (83%) procedures were skin sparing mastectomies and 8 (17%) were modified radical mastectomies. Forty-eight reconstructions were immediate, and 1 delayed. The average TE capacity was 565 cc (450 – 850cc). Initial averaged NS injection was 128 cc (65-260cc). Complications rate: seroma – 2%, hematoma – 0%, partial skin necrosis – 6.2%, superficial epidermolysis – 2%, lateral displacement of TE- 0%, TE failure – 6.2%, cellulites -6.2%, pain 4.2 (on analog score (1-10), minimal capsular contracture Baker'sII 10% at average of 4 months follow-up. Histology of the allograft at 6 months in two cases showed a viable fibrous vascular tissue. Degree of satisfaction 9 (on a scale from 1 to 10). Conclusion: The acellular human dermis allograt (Alloderm) is excellent for closure of the sub-pectoral pocket in breast reconstruction with tissue expanders. It maintains proper support of the fully inflated tissue expander without lateral displacement. The patient has immediate satisfaction with some breast volume and cleavage appearance, with a low rate of complications. |
|
View Synopsis (.doc format, 440.0 kb)

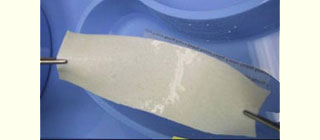 Figure 1: Acellular cadaveric dermis (Alloderm) after soaking in normal saline
Figure 1: Acellular cadaveric dermis (Alloderm) after soaking in normal saline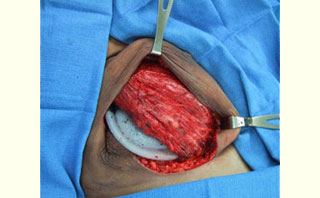 Figure 2: Immediate placement of Tissue Expander (TE) after mastectomy in the subpectoralis space
Figure 2: Immediate placement of Tissue Expander (TE) after mastectomy in the subpectoralis space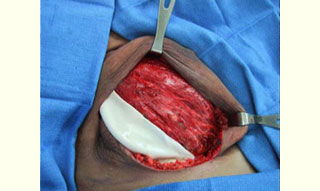 Figure 3: Acellular cadaveric dermis placed in the lateral edge of the pectoralis major muscle
Figure 3: Acellular cadaveric dermis placed in the lateral edge of the pectoralis major muscle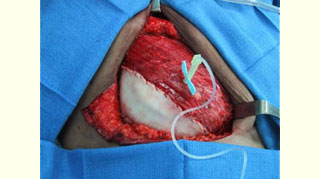 Figure 4: Acellular cadaveric dermis sutured with a straight running 3-0 Vycril to the lateral edge of the pectoralis major and serratus anterior muscles and initial injection of normal saline
Figure 4: Acellular cadaveric dermis sutured with a straight running 3-0 Vycril to the lateral edge of the pectoralis major and serratus anterior muscles and initial injection of normal saline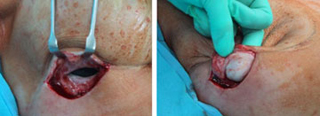 Figure 5: View of the well-integrated expanded Alloderm at the exchange of the TE for a permanent implant (at 6 months)
Figure 5: View of the well-integrated expanded Alloderm at the exchange of the TE for a permanent implant (at 6 months) 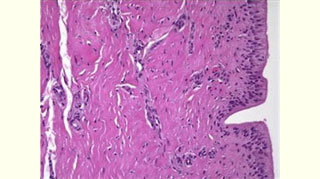 Figure 6: Histology of expanded Alloderm at 6 months: viable fibro vascular tissue
Figure 6: Histology of expanded Alloderm at 6 months: viable fibro vascular tissue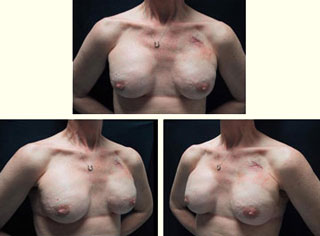 Figure 7: Final result of total skin-sparing mastectomy for breast carcinoma and reconstruction with Alloderm, TE and saline implant
Figure 7: Final result of total skin-sparing mastectomy for breast carcinoma and reconstruction with Alloderm, TE and saline implant