Wednesday, November 6, 2002 - 8:15 AM
721
The Bipedicle Opposing Box (BOB) Flap: The Answer to Nipple Reconstruction Across a Mastectomy Scar
Problem: A mastectomy scar crossing the desired position for proposed nipple reconstruction can limit the desired nipple position because of less than optimal blood supply resulting in partial nipple loss or lack of long term projection.
Purpose: To create a flap that has dual pedicles. The bipedicle opposing box (BOB) flap provides blood supply across a mastectomy scar, thus allowing maintenance of projection, reliability, versatility, and a range of sizes.
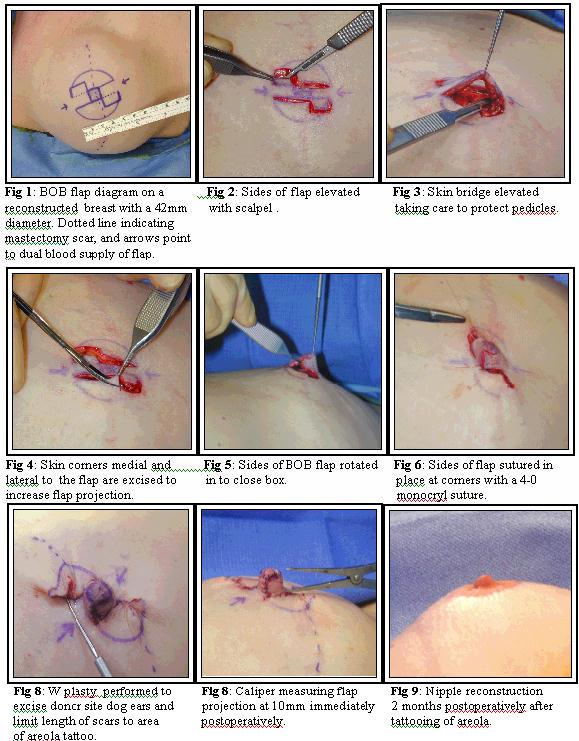
Technique: See photos labeled below. Fig 1: The BOB flap diagram is drawn on a reconstructed breast with a diameter of 42mm. The dotted line is over the mastectomy scar, and arrows indicate the dual blood supply of the flap. Fig 2: The sides of the flap are then elevated with a scalpel. Fig 3: The skin bridge is elevated taking care to protect the pedicles. Fig 4: Corners of the skin medial and lateral to the flap are excised to increase flap projection. Fig 5: The sides of the BOB flap are rotated in to close the box. Fig 6: The sides of the flap are then sutured in place at the corners with a 4-0 monocryl suture. Fig 7: W plasty is performed to excise donor site dog ears and limit length of scars to area of future areola tattooing. Fig 8: Epidermis reapproximated with 5-0 fast absorbing suture. Calipers measuring flap projection at 10mm immediately postop. Fig 9: Nipple reconstruction 2 months postoperatively after tattooing of areola.
Methods: All patients have been photo documented preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperatively in a standardized manor. Objective measurements of flap design, intraoperative projection, and postoperative projection are documented.
Data: To date 20 nipples in 10 patients have been completed. There has been no acute flap loss, immediate loss of projection, or infections. Short term follow up to 2 months shows minimal loss of projection. All patients will be at least 6 months postoperative at time of presentation. All data will be tabulated in an objective manner, including measurements and standardized photography.
Summary: Uniquely the BOB flap provides a dual blood supply to the reconstructed nipple. This technique is reliable while providing good projection, is technically easy to master, and allows variance in size of nipple base and projection. Lastly the reconstructive surgeon will no longer be limited to nipple position by mastectomy scars.
View Synopsis (.doc format, 493.0 kb)
See more of Breast (Cosmetic and Reconstructive)
Back to 2002 Complete Scientific Program
Back to 2002 Meeting home
