Tuesday, September 27, 2005
8019
Assessing the Deflation Rates of 500 Pre-filled Textured Saline Breast Implants Versus 500 Standard Textured Saline Breast Implants: Is There a Difference?
Purpose: To date, no large study of the deflation rates of PIP pre-filled textured saline breast implants has been published. This study provides the first large volume (1000 implant) comparison of the deflation rates of PIP pre-filled textured saline breast implants versus a control group of Mentor Siltex textured saline implants. The goal of this study is to determine whether PIP pre-filled textured implants deflate at a significantly higher rate than Mentor Siltex implants.
Methods: A consecutive series of 500 PIP pre-filled textured saline breast implants was compared to a consecutive series of 500 Mentor Siltex breast implants. Each breast implant was evaluated for a four-year period, and the annual deflation rate (number of deflations during a given year divided by the total number of implants) and cumulative deflation rate (cumulative total of deflations through a given year divided by the total number of implants) were recorded. Statistical significance was calculated with a chi square analysis.
Results:
The results of the PIP implant series are given below:
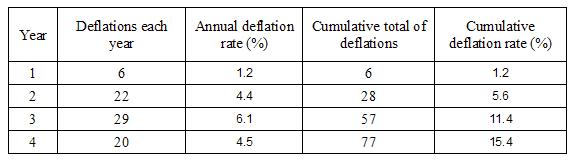
The results of the Mentor series are given below:
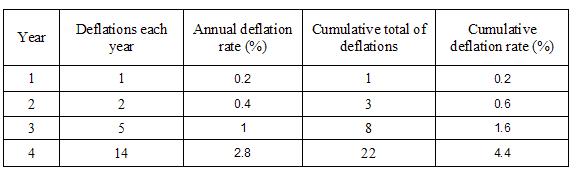
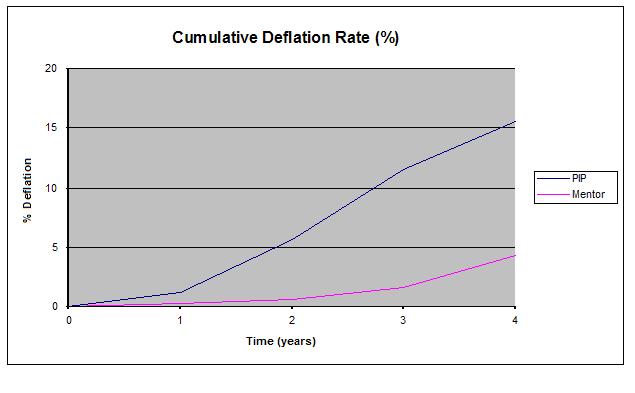
At year 1, the difference between the cumulative deflation rates is not statistically significant at the a= 0.05 significance level (chi square 2.30, p >0.05); however, at year 2 (chi square 13.29, p<0.001), year 3 (chi square 37.91, p<0.001), and year 4 (chi square 32.69, p<0.001) higher deflation rate of the PIP implants versus the Mentor implants is statistically significant.
Discussion: Our data clearly indicates that there is a statistically significant difference between the overall deflation rates of PIP pre-filled textured saline breast implants and Mentor Siltex breast implants at year 2 (p< 0.001), year 3 (p< 0.001), and year 4 (p< 0.001). After 4 years, the 15.56% cumulative deflation rate of PIP implants was over 3.5 times higher than the 4.31% deflation rate of the Mentor Siltex implants. There may be several factors contributing to the higher deflation rate seen in PIP implants, including possible in-vitro deflation before implantation and silicone shell curing technique. Regardless, this statistically significant deflation difference must be taken into account when balancing the risks and benefits of PIP breast implants.
