McCormick Place, Lakeside Center
Sunday, September 25, 2005
9:00 AM - 5:00 PM
McCormick Place, Lakeside Center
Monday, September 26, 2005
9:00 AM - 5:00 PM
McCormick Place, Lakeside Center
Tuesday, September 27, 2005
9:00 AM - 5:00 PM
McCormick Place, Lakeside Center
Wednesday, September 28, 2005
9:00 AM - 5:00 PM
8411
Inframammary Fold Creation in Breast Reconstruction
1. Purpose: To address the importance of the inframammary fold in autologous breast reconstruction using free tissue transfers.
2. Introduction
Autologous breast reconstruction is commonly performed after mastectomy for its natural shape, projection, and feel. A natural inframammary fold in the reconstructed breast is considered to be an essential aspect of achieving an optimal result although there is no data to support this notion. This study addresses whether formation of an inframammary fold during free TRAM breast reconstruction is needed to maintain the shape and placement of the flap.
3. Methods and Materials
A total of 104 patients underwent breast reconstruction with a free TRAM flap from 1995 to 2003. Patients were divided into three groups. One group (N=25) had no suture fixation of the inframammary fold. The second group (N=27) had an inframmammry fold created with absorbable sutures (3-0 Vicryl). The last group (n=52) had the formation of the fold with nonabsorbable sutures (3-0 mersilk). The mean follow up for each patient was 3 years.
4. Results
In the group of patients without the inframammary fold creation, there were 4 cases (16%) of flap displacement and 2 cases (8%) of inframammary fold disruption. In the group with absorbable suture fixation, 2 cases (7%) demonstrated displacement of the flap and 3 cases (11%) of partial inframammary fold disruption. In the group with nonabsorbable suture fixation of the inframammry fold there was only one case (2%) partial disruption of the fold. There were no cases of flap displacement.
5. Conclusion
Our data indicate that reinforcement of ligamentous structures for making a definite inframammary fold is necessary to maintain flap placement and shape. We also determined that it should be recreated with nonabsorbable sutures. Preoperative markings and design are essential to achieve breast symmetry and to mark the location of inframammary fold. While performing breast reconstruction the area of the inframmammary fold should not be undermined in order to preserve the zone of adherence.
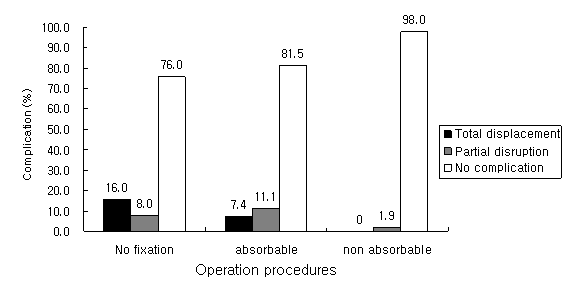
Fig. 1. Comparison between outcomes of different operative procedures.
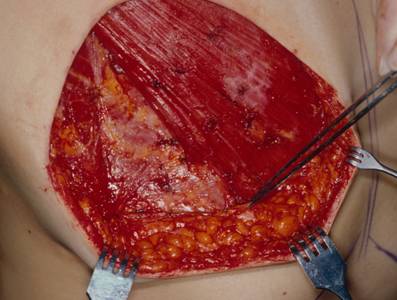
Fig. 2. The ligamentous fold was reinforced or created by internal sutures of dermal layer of abdominal skin to the fascia of rectus abdominis muscle, serratus anterior muscle and pectoralis muscle with 3-0 mersilk.
