Sunday, October 8, 2006 - 1:25 PM
10256
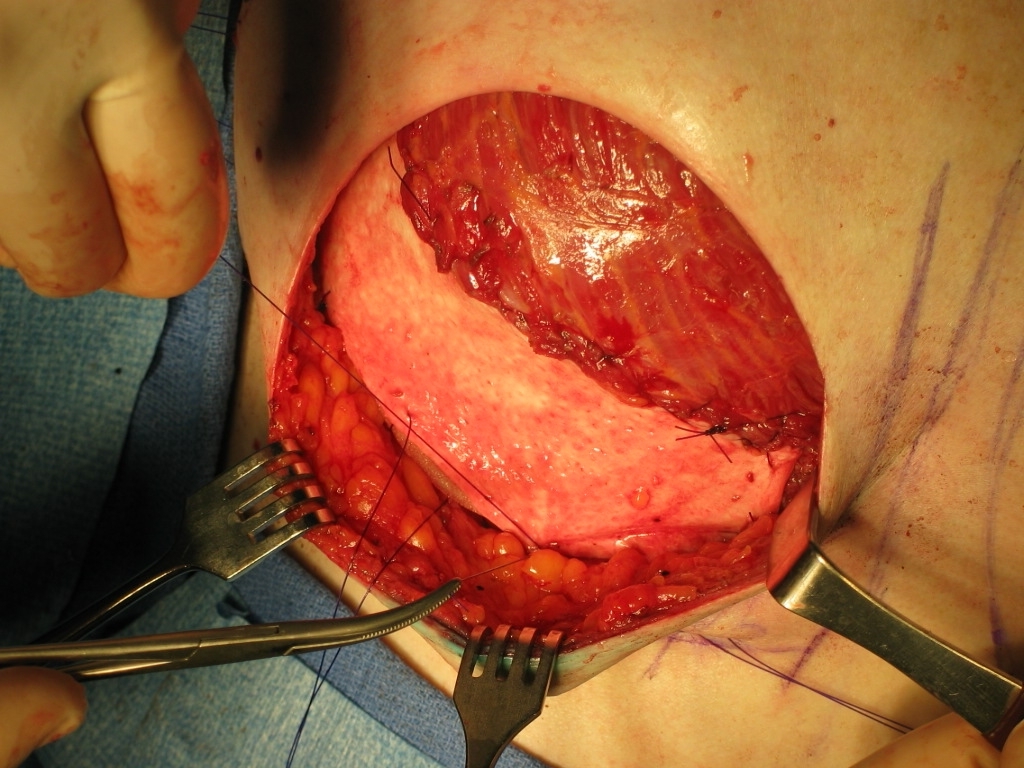
Immediate Breast Reconstruction with Tissue Expanders and Alloderm
Purpose: Prosthetic reconstruction remains the most common technique for breast reconstruction after mastectomy. Dual-plane device placement has been criticized for inadequate control of the lower pole during expansion. One innovation to address this issue has been the insertion of cadaveric dermal graft (Alloderm®) along the inferior border of the pectoralis major muscle. The alloderm sheet anchors the pectoralis major muscle inferolaterally without the need for total sub-muscular pocket dissection. Additionally, the graft defines the inframammary fold, secures the expander pocket, and affords an additional layer of coverage for the device.
Methods: We review 43 consecutive patients from July 2004 to June 2005 who underwent mastectomy and immediate breast with tissue expanders and alloderm. After completing expansion, patients' expanders were exchanged for permanent implants. Postoperative complication rates, time to complete reconstruction, and patient satisfaction were assessed. Parameters of the final reconstructive result were assessed by patients and surgeons using a standardized instrument.
Results: 58 breasts in 43 women were reconstructed with tissue expanders and alloderm. 41 breasts in 30 women completed exchange to implants. Mean time to complete reconstruction was 199 days. Mean follow up was 236 days. Overall complication rate after expander and alloderm placement was 15.5%. Complications included mastectomy flap necrosis(5.2%), cellulitis(5.2%), seroma(3.4%), and explantation(1.7%). There were no complications after exchange to implants.
Conclusions: Cadaveric dermal graft appears to be a useful adjunct in immediate prosthetic breast reconstruction. Use of alloderm has a low complication rate, helps create an aesthetically pleasing breast, and affords an expeditious reconstruction with high patient satisfaction and low revision rate.
View Synopsis (.doc format, 493.0 kb)
See more of Breast (Cosmetic and Reconstructive)
Back to 2006am Complete Scientific Program