Sunday, October 8, 2006
10955
The Use of Bilateral Segmental Ostectomy and Vertical Distraction for the Refinements of Reconstructed Mandible with the Free Fibular Bone Flap
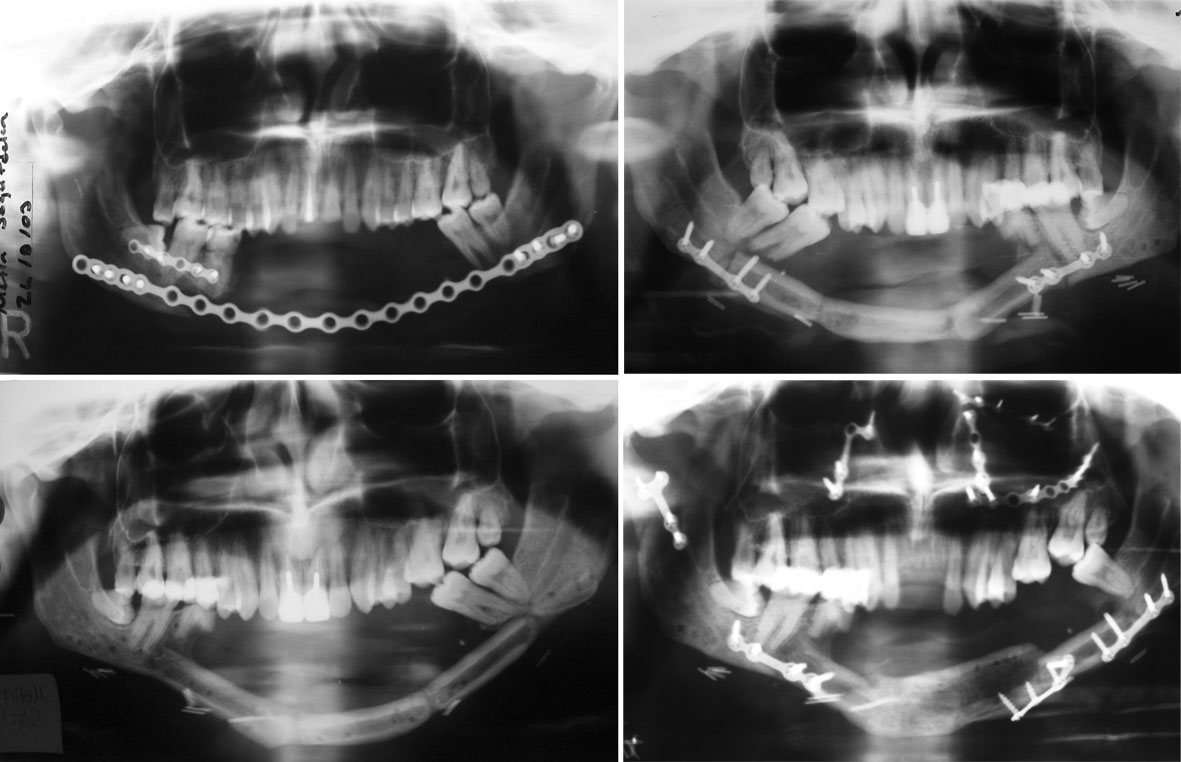
Reconstruction of mandibular bone defects with free fibular flaps have become the method of choice and is indicated primarily for segmental defects of the mandible (1). The residual asymmetry and malocclusion, reported following reconstruction of mandible with free fibula flap,were corrected with a unilateral linear osteotomy at junction of the flap with the mandible (2). Also the vertical deficiency between the reconstructed segment and the occlusal plane made dental rehabititaion imposible in some cases and vertical distraction of transplanted fibular flap can be used to overcome this problem (3,4). We encountered both problems in our patient who had previously mandibular reconstructions with free fibular bone flap due to extensive bone defect result from gun-shot injury(Figure-1). To overcome this, first, we used bilateral segmental ostectomy at the junction of the bone flap with the mandible to set back the free fibular flap in order to correct the malocclusion and prognatism.Later vertical distraction of the fibular flap was performed. CASE REPORT: A set-back operation was performed under general anesthesia. Following the limited subperiostal dissection a vertical ostetomy was performed at both junctions of the fibular flap and the mandible. To correct the prognatism, excess bone segments on both ends of the fibular flap (7 mm bone segment on right side and 8 mm bone segment on left side) were excised. The initial osteotomies on both sides were perpendicular to mandibular plane during the segmental ostectomy. However the second osteotomy, which was mesial to first one, was performed at 15 degrees to first osteotomy line on both sides. This enabled us to move the fibular flap upward in the vertical plane. Then the shortened fibular bone flap fixed with minicompresion plates to the native mandible. Postoperative period was uneventful. The prognatic appearance was no more observed in follow-up period.Due to vertical deficiency in bone height and extensive tissue scaring the prosthetic rehabilitation could not be performed in this patient. Five months after first operation vertical distraction of fibular flap was performed to augment the vertical deficiency. Fibular bone segments (60 mm) were distracted with using extraoral uni-directional alveolar ridge distraction device after a latency period of 5 days. The rate of distraction was 1mm/day and the rythym was 4 times (4X0.25 mm). Distraction was continued till the desired height(10mm) was achieved and the distractor left in place for bony consolidation.However the patient had motorcycle traffic accident which result panfacial fracture on the nineteenth day of the consolidation period. Due to this accident the patient had subcondilar fracture on the right side and fracture of basal bone of the distraction segment on the left side. The patient had open reduction and rigid fixation for the treatment of fractures. Following the surgery consolidation peroid was uneventful ( total 12 weeks) . During the removal of distraction device new formed bone was observed in the entire distraction gap.Later vestibuloplasty was performed. Vertical distraction and vestibuloplasty enabled dental restoration of the patients with mandibular removable partial dentures.The increase of vertical bone height was stable during the 7 months follow-up period.
1. Cordeiro, P.G., Disa J.J., Hidalgo, D.A., and Hu, Q.Y. Reconstruction of the mandible with osseous free flap: A10-year experience with 150 consecutive patients.Plast.Reconstr.Surg.104: 1314,1999. 2. Chang, Y.M., Chana, J.S., Wei, F.C., Tsai, C.Y., and Chen S.H.T. Osteotomy to treat malocclusion following reconstruction of the mandible with the free fibula flap. Plast.Reconstr.Surg.112: 31,2003. 3. Nocini P.F, Wangerin C, Albanese M, et al. Vertical distraction of a free vascularized fibula flap in a reconstructed hemimandible. Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery 28:20, 2000 4. Klesper B, Lazar F, Siessegger M, et al. Vertical distraction osteogenesis of fibula transplants for mandibular reconstruction- a preliminary study. Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery 30:280, 2002 Figure-1: Panoramic radiographs of the patient. (Above,left) After first operation in which reconstruction plate was used. (Below,left) After reconstruction with fibular bone flap. (Above,right)After bilateral segmental ostectomy (Below,right ) After vertical distraction at postoperative 7 months.
View Synopsis (.doc format, 466.0 kb)