Sunday, October 8, 2006
10973
Vertical Distraction Osteogenesis of Fibular Bone Flap in Reconstructed Mandible
Background: Excellent functional and aesthetic results can be achieved by using free fibular flap for the reconstruction of mandibular bone defect(1). Because of the limited diameter of the fibula flap compared with the height of the mandible, vertical distance between the reconstructed segment and the occlusal plane can be substantial. This is a particular problem in dentate mandible, especially when rehabilitation with dental implants or an tissue borne denture is contemplated. The vertical deficiency of fibular flap and extensive soft tissue scar made dental rehabititaion imposible in some cases and vertical distraction of transplanted fibular flap can be used to overcome this problem (2,3). In our 3 patients we encountered this problem. To overcome this segmental vertical distraction of the reconstructed mandible were performed in these patients. Methods: Segmental vertical distraction of the reconstructed mandible were performed for dental rehabilition in 3 patients who had previously mandibular reconstructions with free fibular bone flap due to extensive bone defect result from gun-shot injury. All the patients had a vertical bone deficit of fibular bone flap and extensive intraoral scar that prevent dental rehabilitation. Fibular bone segments (40-70 mm) were distracted with using extraoral distraction device after a latency period of 7 days. The rate of distraction was 1mm/day and the rythym was 4 times (4X0.25 mm). Distraction was continued till the desired height was achieved and the distractor left in place for 12 weeks for bony consolidation.Later vestibuloplasties were performed. Results: During the removal of distraction device, sufficient new regenerated bone was observed in the distraction gap. No minor or major complication such as insufficient ossification or osteomyelitis were encountered. The amount of vertical height achieved after distraction was between 9 and 13 mm(Table-1). The increase of vertical bone height and vestibuloplasties enabled dental restoration of the patients with mandibular removable partial dentures(RPD). it is possible to perform more soffisticated dental rehabilitation with using osteointegrated implants.Health insurance companies do not reimburse osteointegrated implant cost in our country. Therefore, dental restoration was performed in these cases with mandibular RPD. Average follow-up period was 13 (7-22 ) months and during this period the patients used their prosthesis without any problem. The increase of vertical bone height was stable during follow-up period except 1 case however the decrease was observed in 2-3 months postoperatively(remodeling) and then it was stable( Figure-1). Conclusion: Fibular flap, used for reconstruction of the extensive bone defect , can be distracted vertically without any complication in order to overcome vertical deficiency causing difficulties for dental restoration.
REFERENCES 1. Cordeiro, P.G., Disa J.J., Hidalgo, D.A., and Hu, Q.Y. Reconstruction of the mandible with osseous free flap: A 10-year experience with 150 consecutive patients.Plast.Reconstr.Surg.104: 1314,1999. 2. Nocini P.F, Wangerin C, Albanese M, et al. Vertical distraction of a free vascularized fibula flap in a reconstructed hemimandible. Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery 28:20, 2000 3. Klesper B, Lazar F, Siessegger M, et al. Vertical distraction osteogenesis of fibula transplants for mandibular reconstruction- a preliminary study. Journal of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery 30:280, 2002
Table -1 Data on patients' initial bone height, increase in bone height and bone height at the end of follow-up period
|
Patients |
Sex and age |
Length of distracted segment (mm) |
Initial bone height(mm)
|
Increase in bone height (mm) |
Bone height (mm) |
Follow-up (month) |
|
1 |
M/ 23 |
40 |
12 |
9 |
20 |
22 |
|
2 |
M/ 32 |
70 |
13 |
13 |
26 |
10 |
|
3 |
M/ 25 |
60 |
10 |
10 |
20 |
7 |
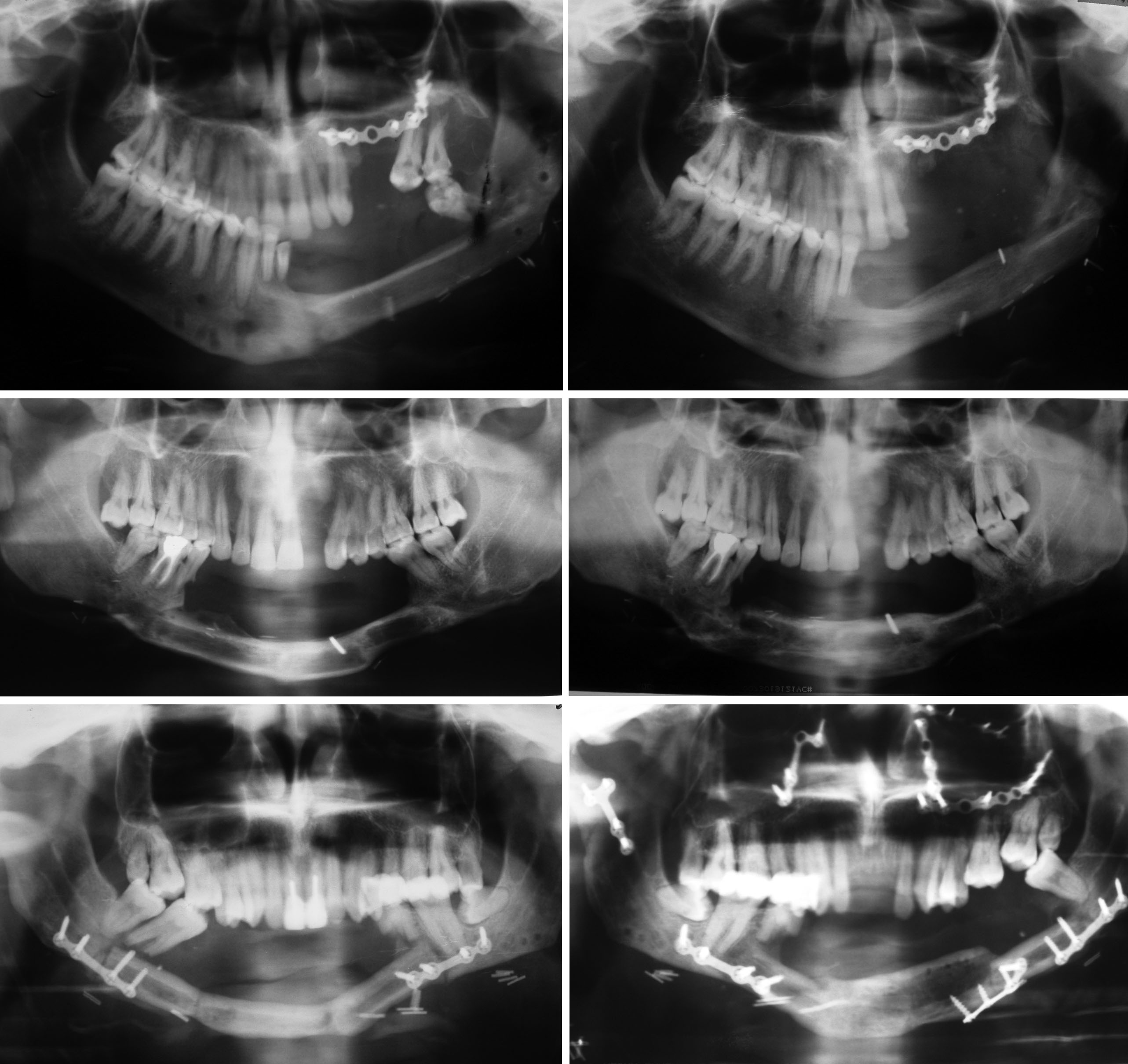
Figure-1 : Preoperative and postoperative (end of the follow-up period) orthopantomograms (Above, right, left) Case I . (Center right, left) Case2. (Below, right,left) Case 3.This patient had motorcycle traffic accident which result panfacial fracture on the nineteenth day of the consolidation period. Due to this accident the patient had subcondilar fracture on the right side and fracture of basal bone of the distraction segment on the left side. The patient had open reduction and rigid fixation for the treatment of fractures.
View Synopsis (.doc format, 30.0 kb)
