Tuesday, November 4, 2008
14512
Autogenous Schwann Cells in Nerve Allografts Indicate that Anti-CD40 Ligand Costimulatory Blockade Induces a Permissive State
Introduction: Schwann cells (SC) are the most antigenic component of peripheral nerve allografts. As such, defining the fate of SC after allotransplantation will define the duration of antigenic stimulation. Experimentally blocking the binding of CD40 to its ligand, CD40L, extends tolerance to nerve allografts. MR1 is an antibody which binds with CD40L thus blocking the CD40-CD40L costimulation pathway. We hypothesize that following nerve allografting, SC are tolerated while being replaced with autogenous SC from the proximal and distal nerve ends if MR1 is administered at the time of grafting. As a functional test of our grafts, we measure differences in muscle contractile maximal forces for the reinnervated extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscles.
Methods: Rosa26Bl/6 mice are a C57Bl/6 mutant strain containing the beta-galactosidase gene that stains SC an insoluble blue. We studied four groups of Rosa26Bl/6 mice (n= 6); three groups received an 8 mm sciatic nerve graft while the Sham group had no graft. The Allograft with saline and the Allograft with CD40/CD40L mAb (MR1) groups each received BALB/c nerve grafts while the Isograft group received C57BL/6 grafts. MR1 was administered IP on day 0 to the allograft with MR1 group while all other groups received saline. On POD 21, extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscles were harvested and maximal isometric force was measured in vitro. The sciatic nerves were harvested and stained by X-gal assay for beta-galactosidase. Histomorphometric analysis of SC was then performed for each nerve graft.Â
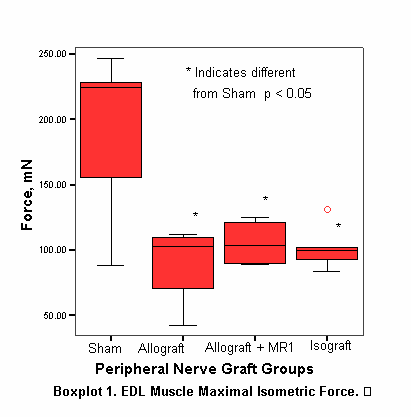
Results: Sham Rosa26Bl/6 nerves contained 1105.2 β-Gal+ SC per 106 µm2 nerve CSA while all other groups showed lower counts of β-Gal+ SC (Table). Isogeneic C57Bl/6 nerve grafts contained 23.5% of the β-Gal+ SC count when normalized to sham group density. Nerve allotransplantation with MR1 averaged β-Gal+ SC counts comparable to that of the isograft group with 181.4% the number of autogenous SC. Nerve allotransplantation without MR1 averaged fewer β-Gal+ SC with only 16.3% that of the isograft group. Boxplot 1 demonstrates the recovery of EDL muscle force for all experimental groups with Sham force > Allograft with MR1 force > Allograft with saline force > Isograft with saline force.Â
Conclusions: Allografts treated with MR1 have 1113% more autogenous SC per 106 µm2 nerve CSA than do allografts treated with saline. SC migration into the nerve graft of allografts treated with MR1 is comparable to that of isografts treated with saline. Recovery of muscle force production following nerve allotrasplantation was improved with MR1 treatment when compared with saline controls. These data are indicative of a permissive state which allows migration of autogenous SC into the nerve graft.Â
Table. β-Gal+ Schwann cells counted in Rosa26Bl/6 mouse nerve grafts 21 days post operative.
|
|
Group |
|||
|
Sham + Saline |
Isograft + Saline |
Allograft + Saline |
Allograft + MR1 |
|
|
n |
3 |
3 |
2 |
3 |
|
SC/ 106 µm2 nerve CSA* |
1105.2 ± 614 |
260.1 ± 233 |
42.4 ± 21.5 |
471.8 ± 347 |
|
% SC migration compared to Isograft + Saline Group |
--- |
100 |
16.3 |
181.4 |
|
*Values shown as mean ± SD. The nerves were cut mid-graft and quantification of SC was done by counting blue (autogenous) cells per 106 µm2 nerve cross sectional area (CSA). SC= Schwann cell |
||||