Saturday, October 2, 2010
18103
Posttraumatic Progressive Orbital Emphysema Treated by Needle Aspiration-Decompression Application: A Case Report
Orbital emphysema is a serious morbidity which occurs with fracture of orbital bone structures and may lead visual loss. Treatment may include different levels such as simple observation and corticosteroid application to surgical decompression.
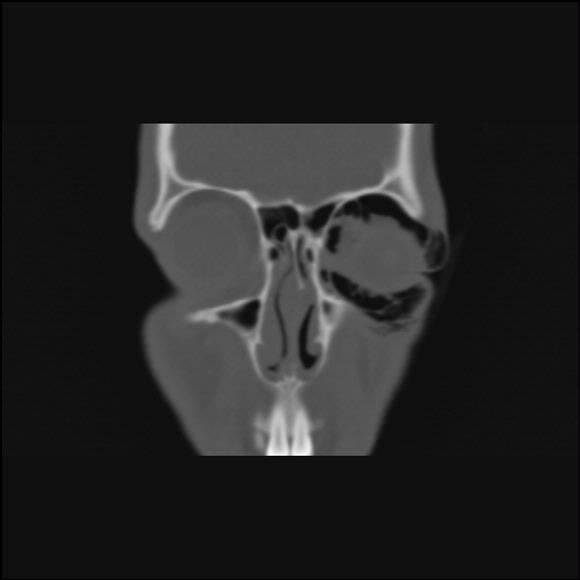
15 years old male patients was applied to our clinic with swelling and pain on his left eyelids due to fist injury. There were no loss of vision or any fracture found on the examination of the patient. Distinct emphysema was found on palpation of the periorbital region. No displaced fracture on the medial wall of the left orbit and orbital emphysema especially filling superior and inferior part of the globe was found on the computerized tomography imaging. Pain with ocular movement and diplopia in lateral gaze developed on patient's follow-up in the clinic. It is observed that the maneuver of the valsalva enhance distinctly both the pain and diplopia in lateral gaze. Therefore percutaneous aspiration-decompression applied with 21 gauge needle under local anesthesia. Patient's complaints were decreased after the intervention. It is observed that the amount of air was disappeared gradually in repetitive computerized tomography imaging.
Orbital emphysema seen after trauma of the facial skeleton is usually benign and limits itself. However the valve effect on the fracture line may cause visual impairment. This situation named as forced orbital emphysema and may cause ischemic optic neuropathy. Decompression treatment is had to do in this situation. Needle aspiration-decompression application like our case is a considerably effective and reliable technique in emergency situations.