Room 2 (Henry B. Gonzalez Convention Center)
Sunday, November 3, 2002
8:00 AM - 4:00 PM
Room 2 (Henry B. Gonzalez Convention Center)
Monday, November 4, 2002
8:00 AM - 4:00 PM
Room 2 (Henry B. Gonzalez Convention Center)
Tuesday, November 5, 2002
8:00 AM - 4:00 PM
Room 2 (Henry B. Gonzalez Convention Center)
Wednesday, November 6, 2002
8:00 AM - 4:00 PM
381
P33 - Induction of HSP47 Protein in Scars
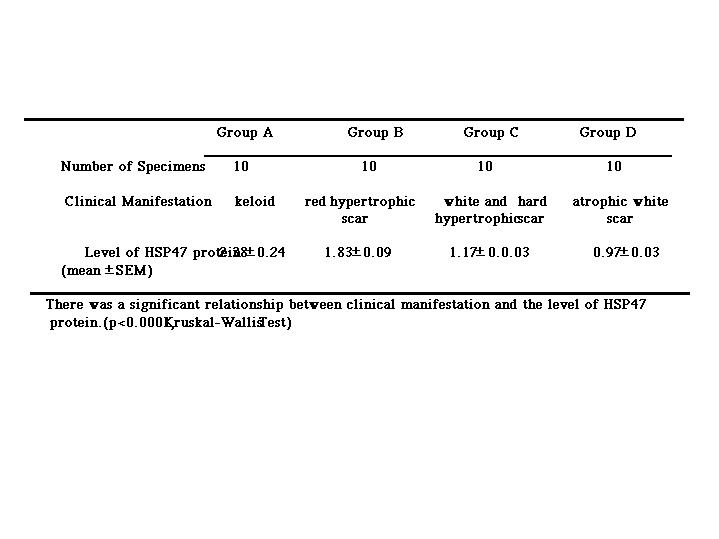
We investigated induction of HSP47 protein, which is an important role in collagen biosynthesis, in keloid, hypertrophic, and atrophic scars. Forty lesions in 37 patients were prepared with normal skin around the lesion resected simultaneously in each case. Resected samples were de-epithelized and HSP47 induction in fibrous tissue was detected by Western blot analysis using anti HSP47 antibody. The level of HSP47 induction of each sample was defined as the relative amount to that of HSP47 induction of normal skin obtained from around each lesion. The 40 lesions were divided into the following four groups according to their clinical features; Group A(n=10); Keloid, Group B(n=10); Red hypertrophic scar, Group C(n=10); White and hard hypertrophic scar, Group D(n=10); Flat or atrophic white scar. The level was 2.38±0.24 in Group A, 1.83±0.09 in Group B, 1.17±0.03 in Group C, and 0.97±0.03 in Group D. There was a significant relationship between clinical manifestation and the level of HSP47 protein. These results may suggest that induced HSP47 protein play some important roles in determination of clinical manifestation of scars
View Synopsis (.doc format, 22.0 kb)
See more of Posters
Back to 2002 Complete Scientific Program
Back to 2002 Meeting home
