Room 2 (Henry B. Gonzalez Convention Center)
Sunday, November 3, 2002
8:00 AM - 4:00 PM
Room 2 (Henry B. Gonzalez Convention Center)
Monday, November 4, 2002
8:00 AM - 4:00 PM
Room 2 (Henry B. Gonzalez Convention Center)
Tuesday, November 5, 2002
8:00 AM - 4:00 PM
Room 2 (Henry B. Gonzalez Convention Center)
Wednesday, November 6, 2002
8:00 AM - 4:00 PM
404
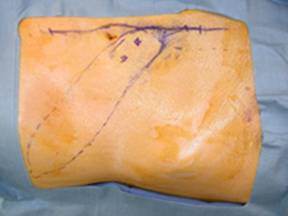
P58 - The Oblique Rectus Abdominis Musculocutaneous (ORAM) Flap: Revisited Clinical Applications
Analogous to the VRAM and the TRAM, the ORAM is a myocutaneous flap with an obliquely oriented skin paddle compared to the long axis of the rectus muscle. Originally described by Drs. Taylor and Boyd, the ORAM skin paddle is based on periumbilical perforators and is aimed towards the tip of the scapula.
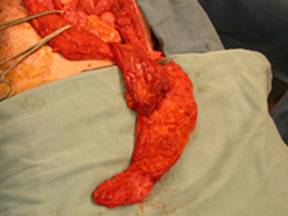
Because of the potential advantages of the ORAM and lack of published clinical studies, we present 8 consecutive successful ORAM flap cases. In seven cases, the ORAM was used in complex perineal and pelvic floor reconstructions involving cancer extirpations and radiated wounds. One ORAM was used as a free flap to the head and neck. Follow up was up to 2 years. All cases resulted in stable wound closure. Fresh cadaveric injection studies were performed to demonstrate the oblique dermatome pattern of blood flow from the periumbilical perforators.
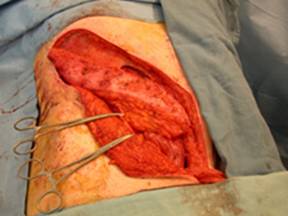
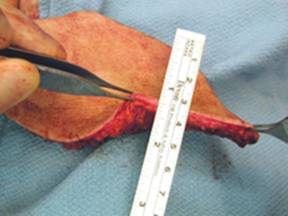
In comparison to other local flaps, the ORAM has several advantages. The distal tip of the flap is located in the midaxillary line over the lower rib cage, and this skin is thin and typically scarfree. The VRAM skin in the upper abdomen is much thicker, and the donor defect more difficult to close. The thin distal tip skin simplifies flap inset, especially for perineal defects. The tip has been reliable in all 8 cases. As a deepithelialized flap, the soft tissue is adequate to fill a radiated pelvic defect, without any expected late muscle atrophy as seen in a pedicled rectus flap. The rectus muscle and anterior fascial dissection is the same as a free TRAM flap, as opposed to the greater muscle dissection of the VRAM. The flap arc of rotation can reach the perianal skin in the perineum and the distal thigh in the leg.
See more of Posters
Back to 2002 Complete Scientific Program
Back to 2002 Meeting home