Sunday, October 10, 2004
6170
The perforator based reversed adipofascial flap for reconstruction of lower leg defects
Purpose: Defects of the lower leg and the foot still remain to be a challenge to the reconstructive surgeon. Due to the lack of alternatives, free flap surgery was often necessary to cover defects in this area, especially if they are located in the lower third of the leg. This report deals with indications, limitations and results of coverage of lower leg defects with distally based reversed adipofascial flaps.
Materials and Methods: From February, 1997 to December, 2003 reconstruction of soft tissue defects of the lower leg was carried out in 25 patients with a mean age of 44 years (3-84 years) with distally based reversed adipofascial flaps, which were based on perforators of the anterior or posterior tibial or the peroneal artery. In the majority of cases tissue loss had resulted from trauma (19 cases). 4 cases were due to infection and 3 cases due to skin necrosis following total knee replacement surgery. The flaps were covered with a split thickness skin graft and the donor area was closed primarily.
Results: All flaps survived. Minor complications involved partial loss of grafted skin (3 cases) and wound dehiscence of the donor site (2 cases). These patients were managed successfully with minor revisional surgery.
Conclusion: Perforator based reversed adipofascial flaps are distinctly different from flaps based on the sural nerve or the lesser saphenous vein. In contrast to random pattern flaps the perforators are capable of supplying enough perfusion to the whole adipofascial flap. The flaps are superior to free flaps as to safety, ease of dissection and operative time. As only adipofascial tissue is contained, the donor site skin can be used for primary closure resulting in a rather inconspicuous linear scar. There is only one operative field and the results are esthetically pleasing with minimal donor site morbidity. Major vessels are preserved.
Reversed perforator based adipofascial flaps are not indicated in cases of infection (e.g. osteomyelitis), with a large defect cavity, in the reconstruction of the weight bearing area and with poor blood circulation (severe diabetic angiopathy and atherosclerosis).
We conclude that reversed perforator based adipofascial flaps are a valuable tool in the reconstruction soft tissue problems of the lower leg including foot and ankle. In many instances they represent a better option than free flap coverage.
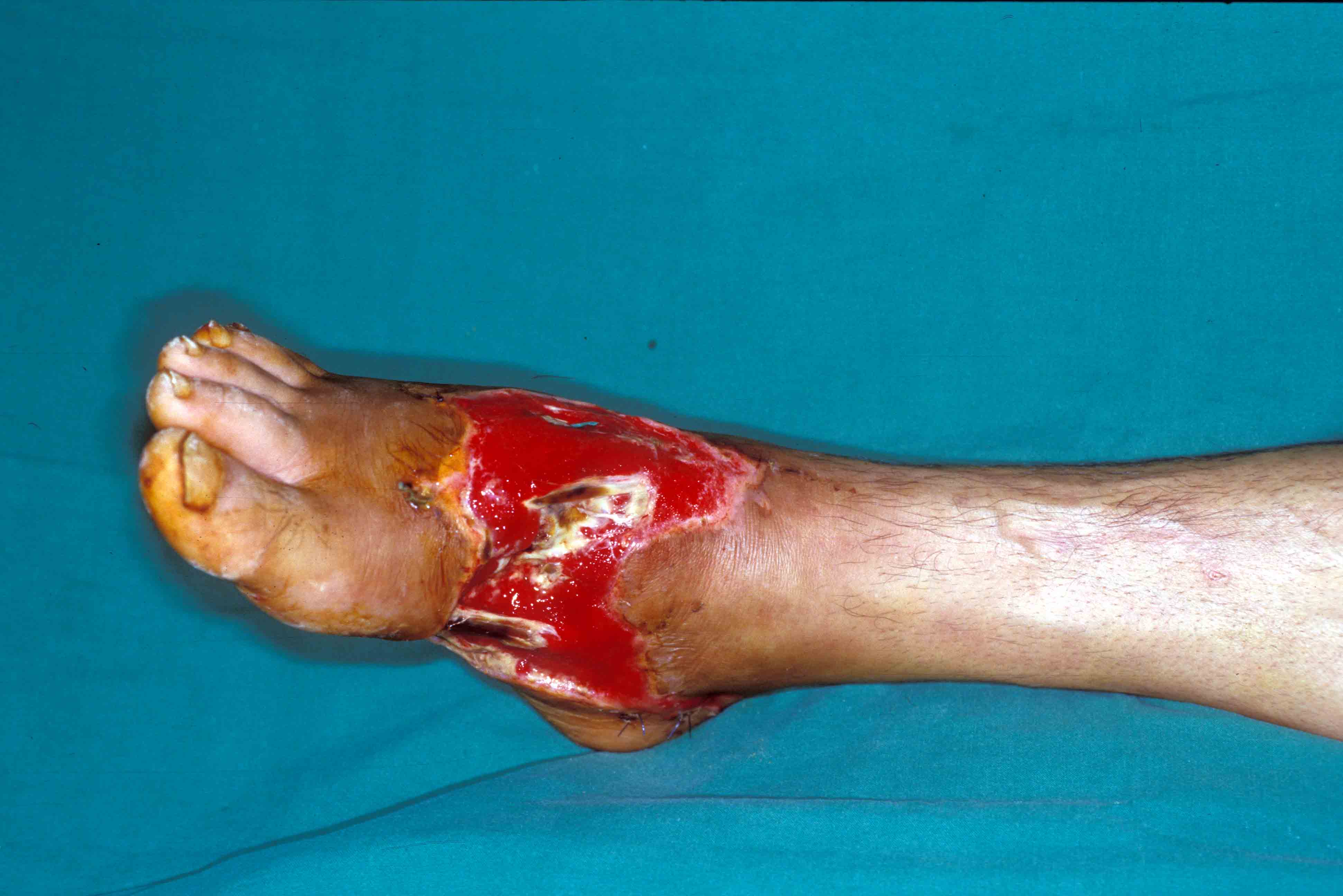
Fig.1: Large soft tissue defect of the right dorsum of the foot with exposed tendons .
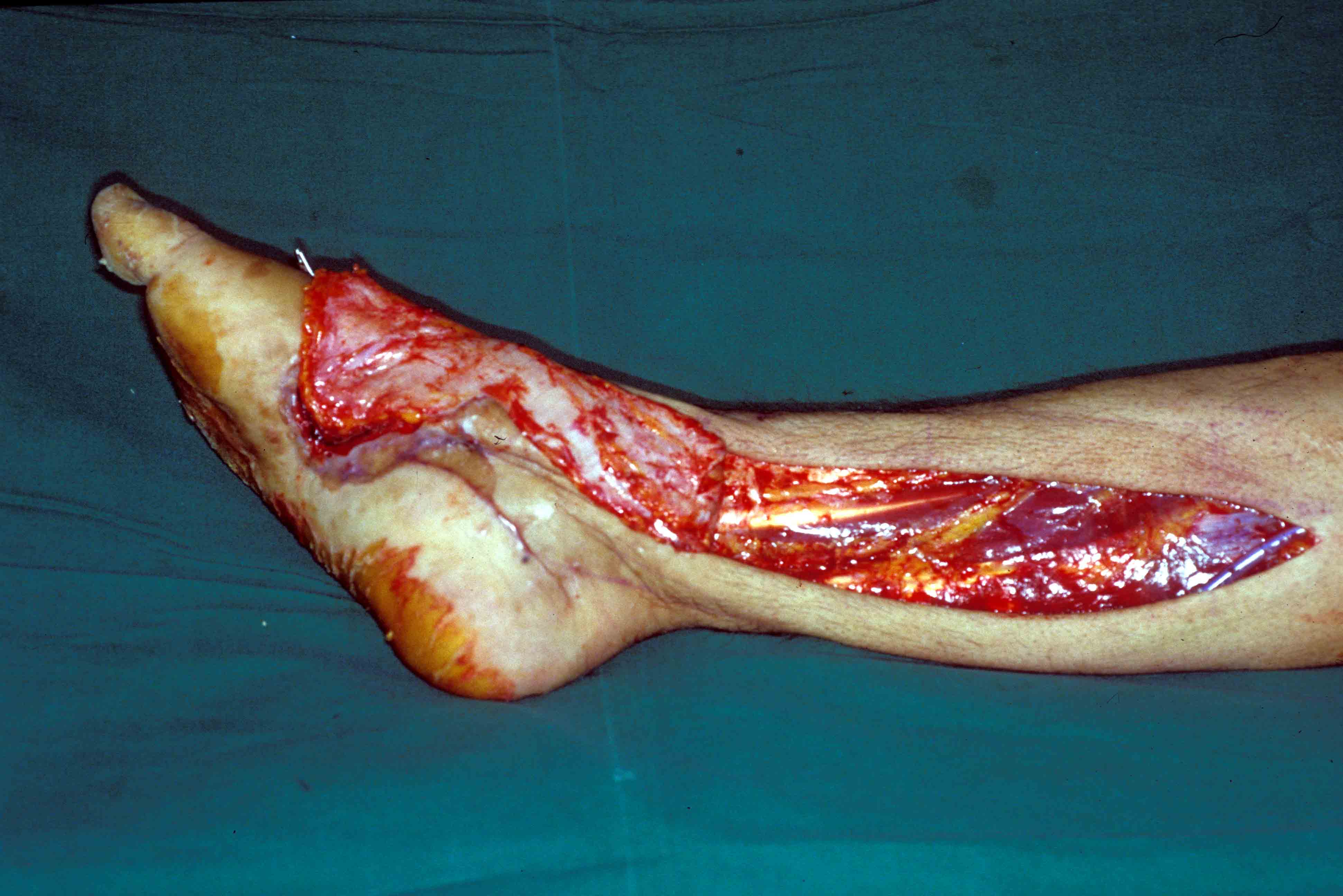
Fig.2: Reversed adipofascial flap based on the posterior tibial artery.
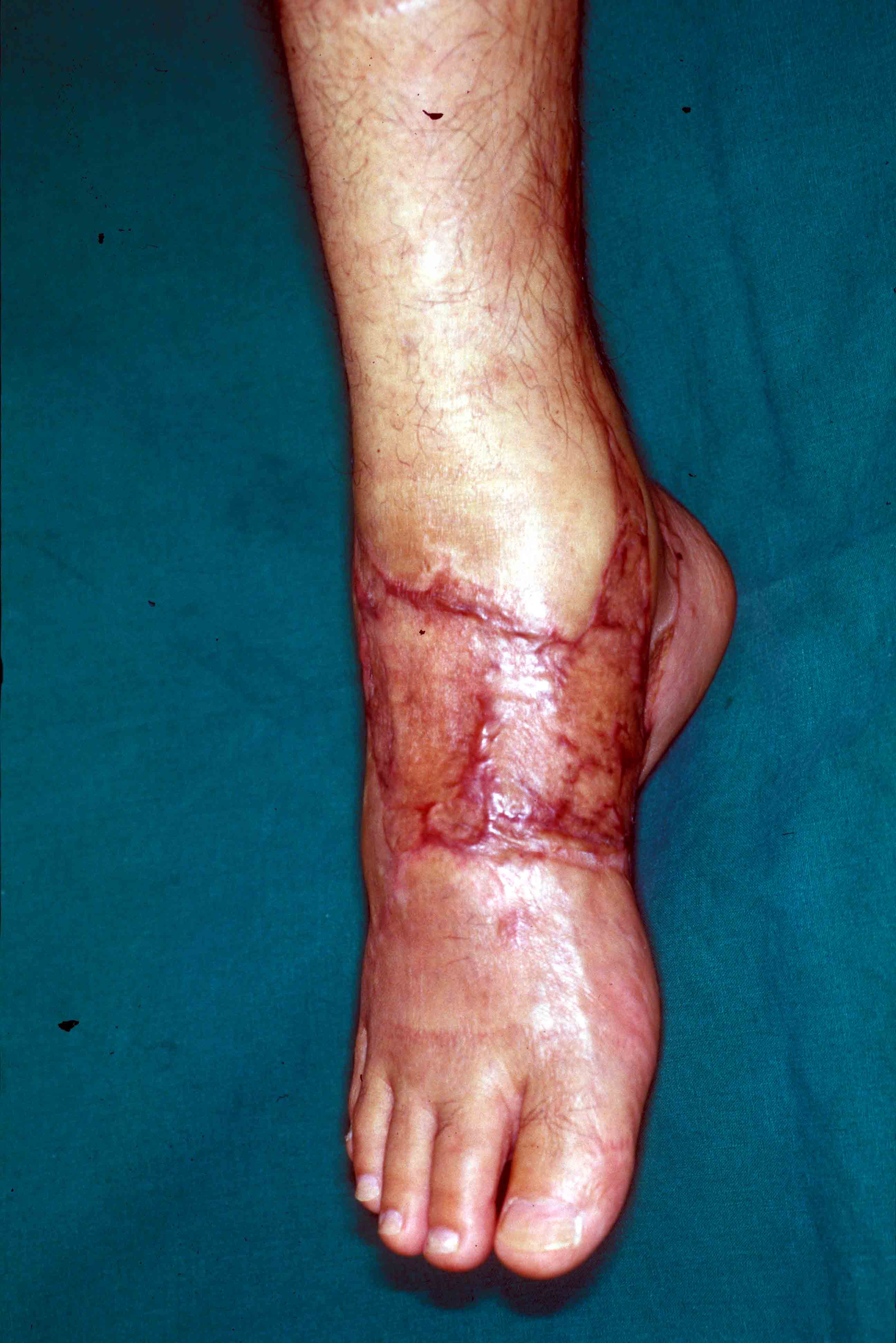
Fig.3: 6 weeks postop result
View Synopsis (.doc format, 341.0 kb)